As cited by Government of India (2015), the aim of smart cities is to provide essential infrastructure, a decent standard of living for its citizens, and a clean and sustainable environment through the application of smart solutions. However, the meaning of smart city could be different for different citizens depending on their socio-cultural and economic realities. We must be able to inculcate all such variations of contextual realities in our urban spaces. To achieve this, the practitioners and academia must steer away from the proverbial ‘technology-centric’ approach and apply design thinking principles to create/retrofit ‘citizen-centric’ urban spaces. To do so, citizens must be included in the process of urban planning. The proposed training strives to expose our learners to various toolkits to achieve these participatory modes of enabling a city’s transition towards being a ‘smart city’. Before doing so, it gently aims to explain the foundation principles of smart cities too.
Objectives of the course
The learners would be able to:
Number of Days : Preferably two weeks
Target Audience : Probationers , City Leaders/ Mayors, City Planners & Researchers
Description on Modules
Module 1: Understanding Building Blocks
1.1 Overview of Governance
(Pre-Read 1: The 17 Goals- sdgs.un.org
Group Exercise1 : Post-Covid Governance Concerns of Developed Countries - and Developing Countries- Mass Migration, water shortage, overcrowding, slums ; Reverse Migration – Shelters, PSD, Transport etc )
1.2 Resolving Governance Concerns by Design Thinking
(Pre-Read 2 - Case Studies of Digital Platforms for Public Policy Formulation - reach.gov.in - Singapore , myGov.in – India
Group Exercise 2 : Identifying and Analysing Digital Platforms to Capture Voices of All so as to build contextualised and personalised spaces)
1.3 Digital Disruption in Governance by Emerging Technologies
(Pre-Read3 – Role of ICT in Governance; Theme Paper IIPA @2019 )
Module 2: TRENDS of DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION IN URBAN SPACES
2.1 Local Municipal Governance and ICTs
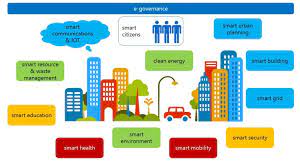
2.2 : Key Components of Smart Cities
( Pre-Read : Smart City Collaboration Model : A case Study of University-City Collaboration ; researchgate.ne;
"Impact of GIFT City & Brief Study of it’s Infrastructure", International Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research (www.jetir.org | UGC and ISSN Approved), ISSN:2349-5162, Vol.5, Issue 11, page no. pp1038-1042, November-2018, Available at : http://www.jetir.org/papers/JETIRK006158.pdf)
(Mini Exercise – Analyse, using TELOS the Relevance of Some Smart Applications in Indian Context : Smart streetlights, Parking sensors, Garbage sensors and automated waste collection)
2.3: Understanding How it is Implemented– Case Studies of Smart Cities
( Pre-Read :
Class Discussions : Identify all the Related Institutional Arrangements eg The Smart City Council, Regulations – PURA, AMRUT and Mandate of GoI eg: 100 Smart Cities)
2.4 : Discussions on Mini Project - Designing @MyOwn City of Dreams
MODULE 3: REALITY : DIGITAL or SMART?
( Pre-Read : Changing nature of CyberCrimes and CII; GoI Cyber Initiatives and Organisations
Class Discussions: Headwinds and TailWinds to Vision of SmartCities , Centre Director (eGovernment Leadership Centre) at ISS, National University of Singapore)
Class Exercise : Develop a PEST Political, Economic, Social and Technical matrix with all possible indicators that must be present while retrofitting a city to be smart)
MODULE 4 : Mini Project - Designing @MyOwn City of Dreams
Identify any city , identify its signature style and issues and redesign it
Assure – Your City has following features:
Capacity Building & Social Awareness